You worked long and hard on your sales plans. You crunched the numbers from last season. You projected into the future. You identified what inventory needed to be in stock. You nailed down the when and where of your supply chain. It all seemed so beautifully planned.
But here it is:
Your 10th, 20th, maybe even 30th customer complaint: That the one thing they want is out of stock.
Is effective inventory management—having exactly the products you need in-stock at exactly the right times, regardless of the season or trend, and therefore creating a rock solid merchandise plan—an impossible task?
It doesn’t have to be.
Table of contents
- What is merchandise planning?
- Understanding merchandise planning in the retail industry
- How to develop a merchandise plan
- Why is merchandise planning important?
What is merchandise planning?
Merchandise planning is a systematic approach to planning, buying, and selling merchandise based upon consumer demand. It means that if a customer wants to buy product X with color Y and size Z from your shop, you have that available when they come knocking.
Understanding merchandise planning in the retail industry
Changes in the retail industry have complicated the merchandise landscape. Global sources, tougher competition, and more product variety are a few challenges retailers face. There is one framework that merchandise planners follow to focus on the right things.
The 5 Ps of retail merchandising include:
- Price. The pricing strategy of your products and how it affects customers.
- Product. Every feature and benefit customers experience from using your product.
- Promotion. The campaigns you run to build awareness, including ads, social media, email promos and other marketing tactics.
- Place. Where people see your products.
- People. The staff that work for your ecommerce business, including you.
Problems, like lost sales because of stockouts or having excess inventory after the season has ended, is exactly what merchandise planning is meant to solve. The goal is to ensure the right product is available for customers, no matter when or where they shop.
How to develop a merchandise plan
The basic concept of the merchandise planning process consists of three equally important steps:
- Post-season analysis
- Pre-season planning
- In-season adjusting
You can define a season as any time period that you prefer; it largely depends on what exactly you are selling. If it’s Christmas sweaters, your season is only a couple of months; for ice cream, it’s year round (although demand will be higher during the warmer months).
When you’re selling merchandise with wildly different seasons, it makes sense to have separate, more detailed plans for all the product categories in which you’re active.
Other factors that affect the process include the size and structure of your retail business, type of store—outlet, online, omnichannel, etc.—and type of merchandise.
Planning merchandise for a menswear company that has multiple retail locations around the country is vastly different than the same process for a company that is selling tea online.
With tea, your decisions revolve around the types of tea you want to sell and then stocking up on them. With menswear, you have the added fun of forecasting how many suit trousers with length X and waist Y you’re going to sell and at what time of year, and then going through the same process with your whole collection.
Fortunately, while the amount of work that goes into merchandise planning varies tremendously depending on your industry, the basic concepts of how to conduct merchandise planning stay the same no matter how big or small the company.
Step 1: Analyze post-season merchandise
The first step is to understand your performance during the previous sales season. Again, it’s up to you to define how long or short a season is.
What’s important here is to really dive into the data, looking at not only the total number of sales, but going deeper into monthly and even weekly results on an item, category, department, and store basis.
Next, you should compare those numbers to the planned numbers from the same year to gain an understanding of how your actual results measure up. Essentially, what you’re doing is a gap analysis on sales.
It’s important to have the same data available going back multiple sales seasons, as this will give you a better overview of where things are going and is crucial for planning into the future.
When looking at your past and current sales data, take context into account. If sales haven’t grown recently, it could very well be because of something you did, or did not do. (For example, maybe you have closed up under performing retail shops or opened new ones.)
Whenever you’re trying to make sense of the numbers, it’s never advisable to look only at raw data without any context. Your business doesn’t live in a vacuum—everything is connected and plays a role. This means outside forces, like the economy, as well as inside forces, like marketing.
What you’ll end up with is an analysis of not only the numbers but also the context behind those numbers. This will make assortment planning for the future a whole lot easier.
Step 2: Plan pre-season merchandise
This is where the fun begins!
Using data from your previous analysis, it’s time to plan the season ahead. It’s crucial to involve your sales, marketing, and even visual merchandising teams from the very beginning.
Without their input, you’ll miss out on context. For example, you could be looking at historical data that shows steady but not exponential growth for a particular product. You’ll add that multiple and be done with it.
What you might not know is that marketing saw those same numbers, looked at the margins from previous years, and is planning to invest three times the spend this time around.
Good for sales. Not good for keeping up with product.
Another thing to keep an eye on during this phase is the impact that opening new sales channels can have on your business—most notably:
- Wholesale
- Social selling
With new channels, it’s always hard to plan ahead, as you have no actual sales data to back up your assumptions. In a situation like that, it pays to look at channel-specific industry sales data and use that for your projections.
Even when taking all of the above into consideration, there inevitably will be situations where you find yourself with either too much or too little stock. Smart business owners plan for every eventuality, so they have backup plans for everything, and you should too.
When they run into overstock issues, they have plans for getting rid of it. That can mean creating a special newsletter with bargain prices for things that are not selling, or using secondary markets like eBay, discount scripts, or flash sales.
The concrete tactics are up to you; the idea is to have a plan for when those situations arise so you’ll know exactly what to do. When the problem is that you have more orders than you have stock, companies that dropship can be your savior.
Step 3: Adjust in-season merchandise
Big-box stores like Target and others have realized that the way supply currently is managed is dead, and there are smarter ways powered by new technology to take care of that.
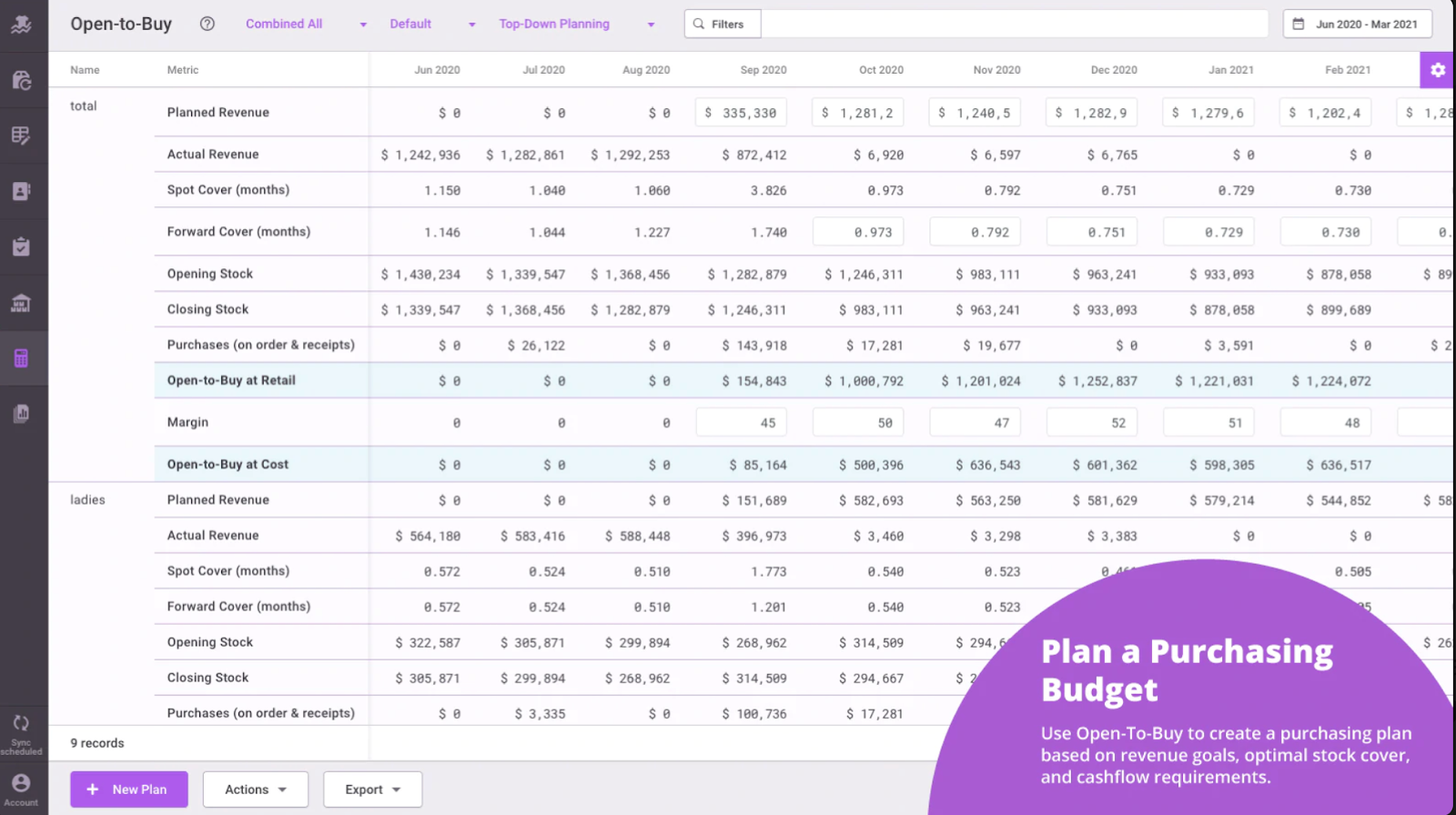
The technology is called “open to buy,” or OTB for short.
OTB is a financial planning tool designed to make it easier for businesses to manage inventory. It helps avoid both overbuying and underbuying by making sure the product is always available.
An OTB system looks at your current inventory plus your planned sales, and compares that data with data from your actual sales. The system then makes automatic adjustments to your future purchase orders to make sure you never run out or that you don’t overstock on items of which you already have plenty.
Many inventory management systems have OTB either built in or available as an add-on. As there are so many different systems, it’s hard to provide links or more concrete information on all of them. Your best bet is to talk with your system provider directly.
Shopify Plus’s APIs make it fairly easy to integrate with many OTB systems. There also are many good ready-to-run OTB apps, such as Inventory Planner. You can get reliable, real-time data with these apps and automate replenishment decisions easily.
Why is merchandise planning important?
By using merchandise planning, you can anticipate changes in market demand and adjust product availability accordingly, ensuring the right merchandise is available in the right quantities at the right time.
It’s also important for retailers to:
- Maintain profits. Data-driven, accurate forecasts help retailers buy merchandise at ideal cost points, so they can better manage inventory costs and reduce markdowns. Planners also collaborate with other partners to develop sales, margin, and product turn plans that drive growth.
- Respond to changes in customer demand. By monitoring trends and balancing store assortment, you can proactively reallocate resources where needed for maximum return.
- Monitor product line performance. Retail merchandise planning gives you insight into customer preferences and marketing effectiveness. You can easily identify underperformers and determine how to optimize product lines for maximum sales.
Overall, merchandise planning helps ensure gross margin and inventory objectives are being met, whether you’re launching new products or getting rid of old stock. It ensures a healthy balance of inventory and manages inventory flow to maximize merchandising strategies and minimize risk.
Effective merchandise planning is critical to successful supply chain management for any size retailer.
Building a centralized inventory management system to satisfy customer demand
Merchandise planning is a crucial step for any retailer, in-store or online. It enables you to take the maximum possible revenue from your inventory, while at the same time balancing stock levels.
It might seem like a complicated process but, in reality, it’s not. It consists of three easy steps:
- Analyze past results
- Plan for the coming season
- Adjust as needed (OTB)
By following these steps, you’ll be well on your way to managing your inventory levels with ease.
Merchandise planning FAQ
What is the merchandise planning process?
A merchandise planning process analyzes consumer demand and develops strategies to maximize your company's sales and profits. It involves analyzing past sales and trends, forecasting consumer behavior, and setting pricing and promotions strategically.
What does a merchandise planner do?
Merchandise planners develop strategies to maximize sales and profits. They pick and price items based on data and trends, ensuring the store's overall financial goals are met. Planners may also use a planogram to visualize SKUs in your retail store and improve visual appeal.
What are the components of merchandise planning?
Merchandise planning is a systematic process that involves several components, including analyzing customer needs and preferences, demand forecasting, creating a merchandise mix that meets customer needs and preferences, pricing products, and monitoring and controlling inventory.
What are the 5 Ps of merchandising?
The five Ps of merchandising are product, price, promotion, place, and people.
Read More
- How Ecommerce Teams Get Buy-in To Sell More
- Why Leading Indicators in Ecommerce Are the Key to Success & How to Find Them
- Shopify Flow Templates you can use During COVID-19
- How to Personalize for Unknown Black Friday Cyber Monday Mobile Visitors
- How to Reduce Post-Holiday Returns
- How to Reduce Fears and Bring Clarity to the Checkout
- How to Block the Ad Blockers & Whether You Should
- What are the retail trends for 2023?
- Wholesale Ecommerce: What is It and How to Start?